Color is an essential aspect of any artwork, and changing the hue of your artwork can significantly impact its overall aesthetic. However, if you’re new to digital art or CSP, you may find the process of changing hue challenging. That’s why we’re here to guide you every step of the way and ensure that you have the necessary knowledge to change the hue of your artwork with ease.
With this skill, you can take your digital art to the next level and create stunning works that capture the eye and the imagination. Let’s get started and learn how to change hue in Clip Studio Paint!
How to Change Hue in Clip Studio Paint
Select the layer that you want to adjust in the Layer Palette.
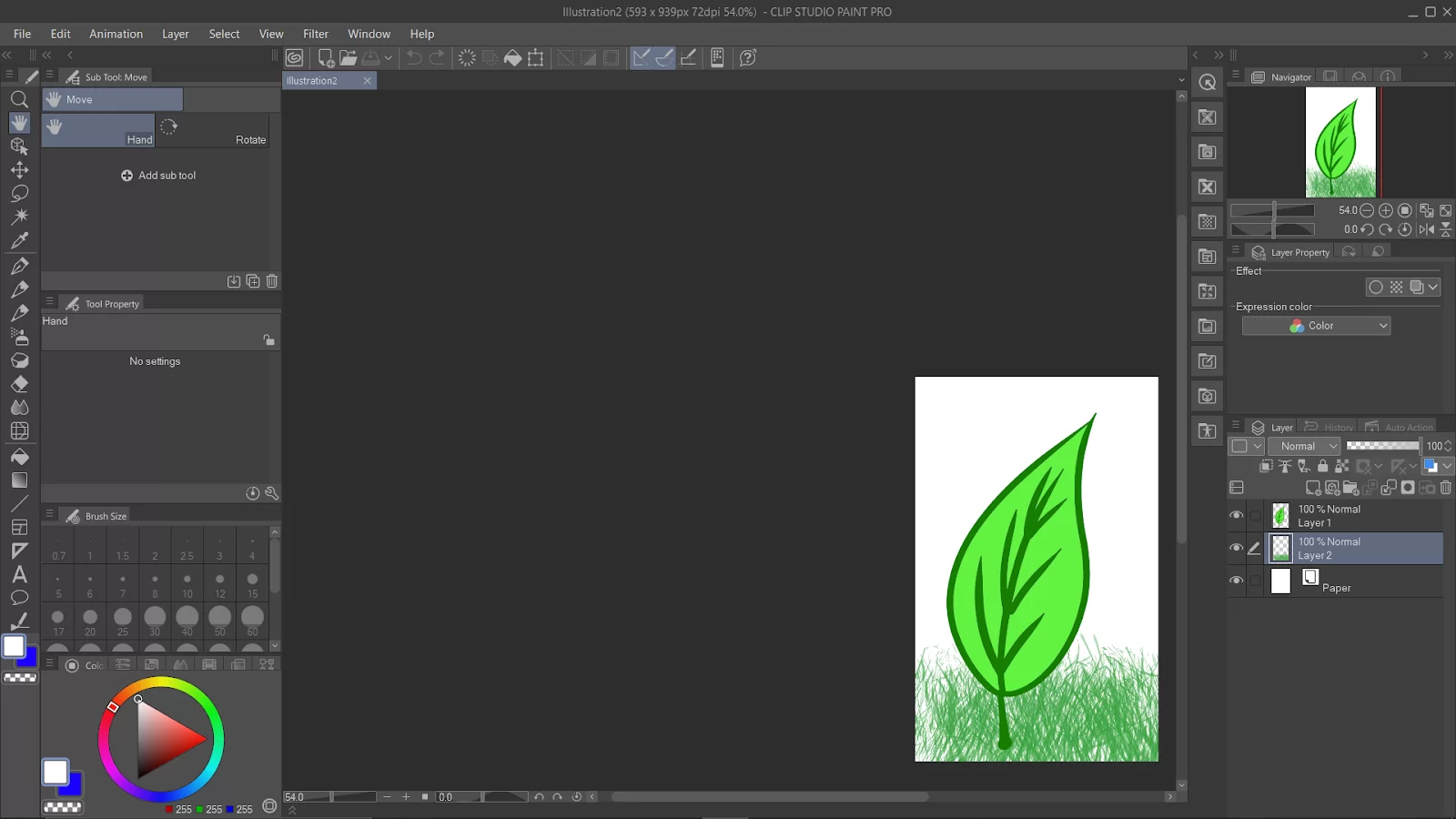
Go to the “Layer” menu and select “New Correction Layer.”
Select “Hue/Saturation/Luminosity” from the list.
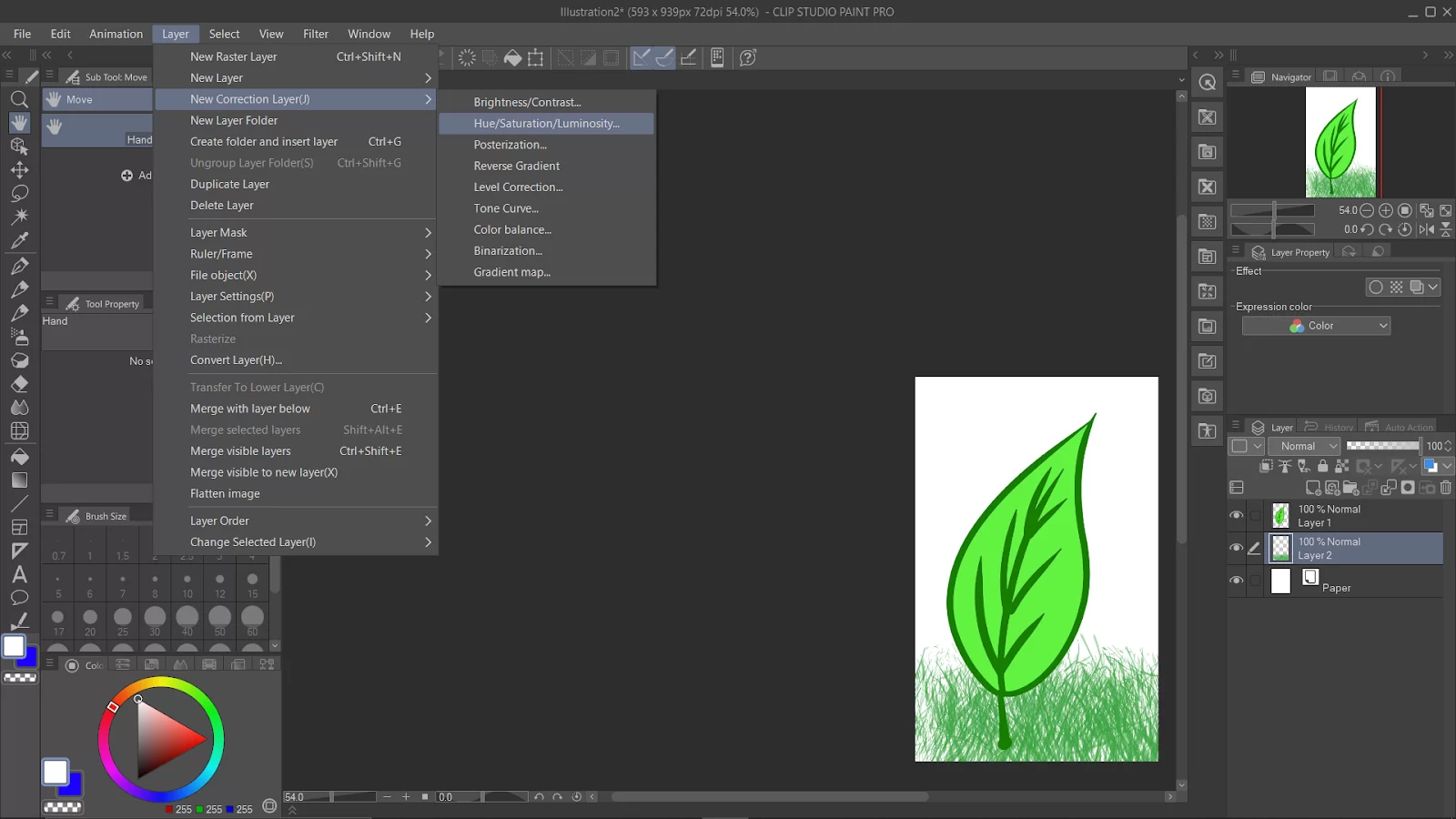
A new “Hue/Saturation/Luminosity” layer will be added to your Layer Palette.
You can adjust the “Hue” slider in the Layer Properties to change the image’s hue. You can also adjust the “Saturation” and “Luminosity” sliders to change the saturation and brightness of the image.
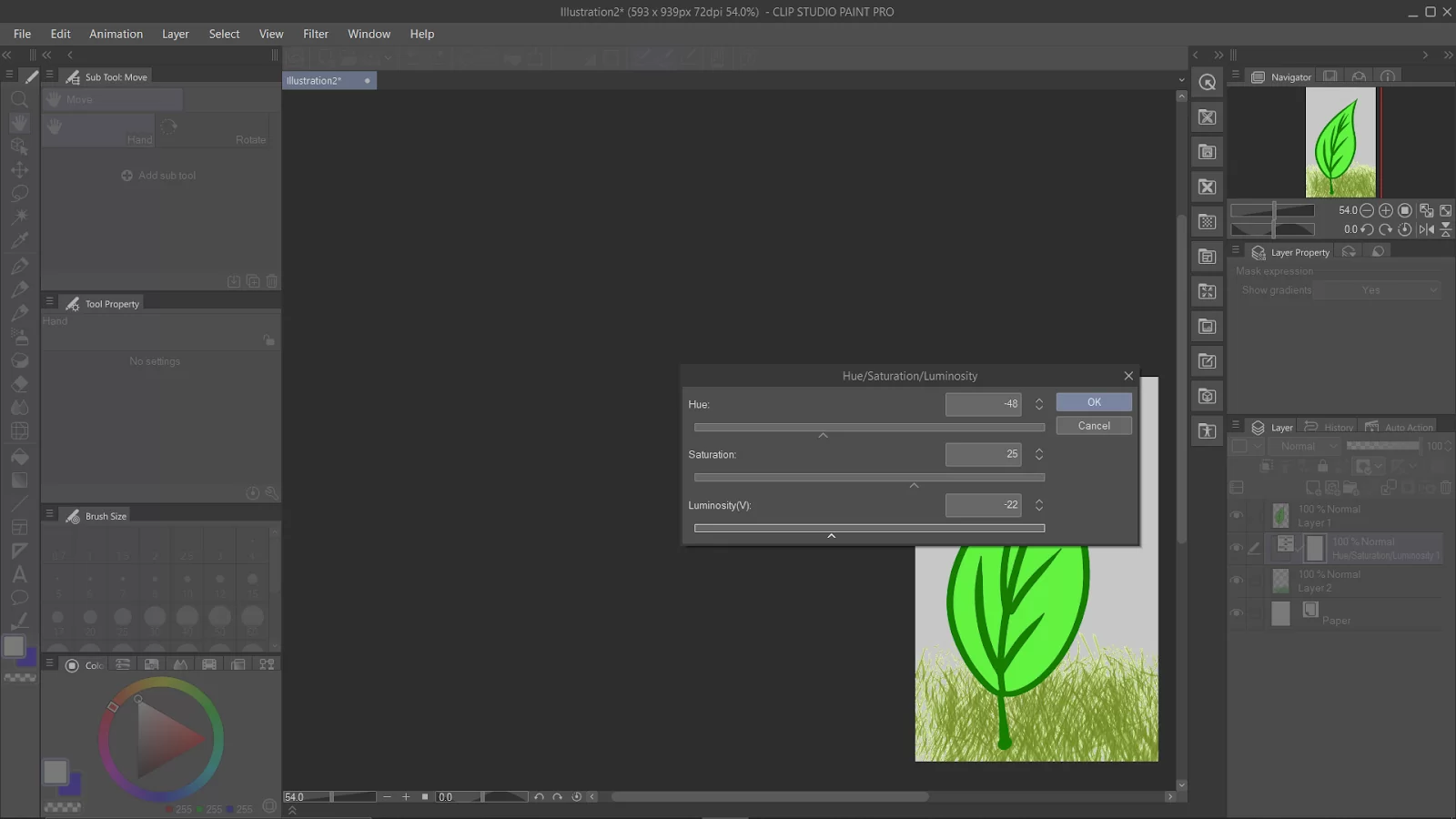
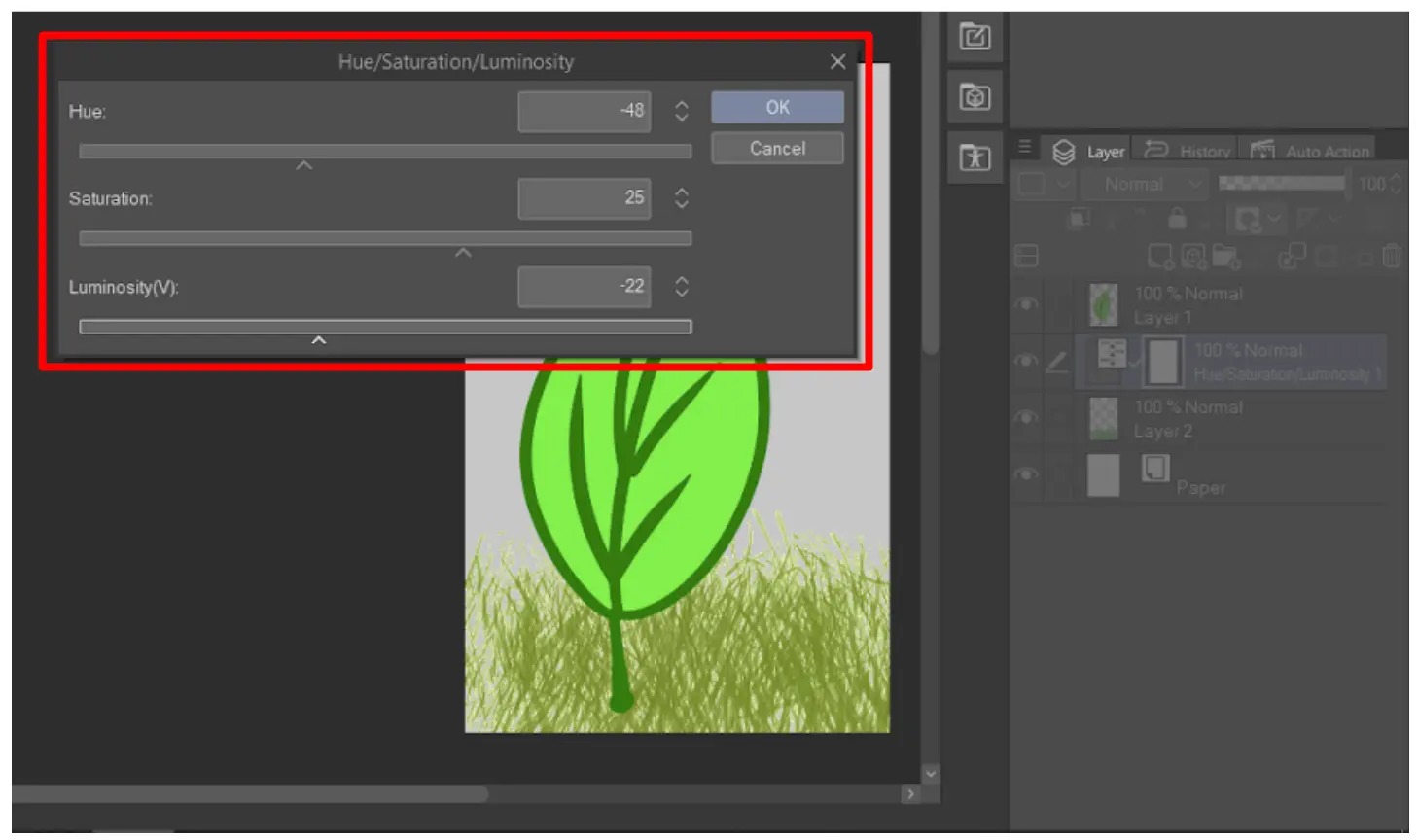
Once you have made your adjustments, click the “OK” button to apply the changes.
Understanding Hue
You won’t be able to effectively use Hue in Clip Studio Paint if you don’t understand the basics of Hue. You first need to understand that Hue isn’t color, and color isn’t Hue. People use these terms interchangeably, but they aren’t the same technically. It is very common, even among artists and designers, to think they both mean the same thing.
Generally speaking, they are similar, but technically, they aren’t. So, what is the difference? Color is the general term. Color describes every Hue, Tint, Tone, or Shade. Black, white, and gray are often referred to as colors. On the other hand, Hue refers to the dominant color family of the specific color you are looking at. Black, white and gray isn’t hues.
If you are imaginative, you can think of hues as colors of the rainbow. If we arrange the colors in a circle, in a sequence from orange, orange-blue, blue-orange, etc., we will end up with a color wheel of the Hues of that color.
Also, when you are thinking about Hues, remember that each hue has different colors that vary in value (dark/light) and chroma (intensity). Even though they vary in value and chroma, they are still part of the same family.
Let us take the blue Hue, for example. In the blue Hue, you can find a wide variety of ranges. In the blue Hue, you’ll find pure blue, light blue, dark blue, high chroma blue, low chroma blue, etc. Understanding these things will help you when you are using that Hue slider in Clip Studio Paint.
Finally, Hue describes where the color that we see came from. The hue can be compared to one of the six primary and secondary colors. In other words, the mixture you’re looking at has a foundation color that is either Yellow, Orange, Red, Violet, Blue, or Green. Capiche?